Feeling dragged out by 3 p.m., stiff after a short walk, or foggy during meetings? You are not alone. Many everyday aches tie back to low-grade inflammation and gaps in nutrition. That is why a simple daily habit can help, like adding omega-3s from fish oil or algae supplements.
Omega-3s are essential fats your body needs for cells, nerves, and the heart. The two heavy hitters are EPA and DHA. You get them from fatty fish, quality fish oil, or algae oil. Your body does not make enough on its own.
So, what happens to your body when you take omega-3 everyday? In short, inflammation cools, joints move easier, and triglycerides trend down. Many people notice steadier energy, clearer thinking, and healthier skin over time. These changes build over weeks, then compound with consistency.
There is more you may feel day to day. Digestion can settle when inflammation calms, and skin may hold moisture better. Sleep can improve too, which boosts recovery and mood, as seen in research on the benefits of omega-3 for better sleep. Small wins here add up across your routine.
This post keeps it simple and practical. You will see what the science says about heart health, brain function, mood, joints, and recovery. You will also learn how much EPA and DHA to aim for, what to expect in week 1 versus month 3, and how to pick a supplement that actually delivers. Let’s set clear expectations so you can get real results without guesswork.
How Omega-3 Supports Your Heart Health Daily
Think of omega-3s as oil for your cardiovascular engine. When you take them every day, your blood moves with less friction, your vessels stay calmer, and your heart works with less strain. That steady support adds up. Over weeks, you may see lower triglycerides, healthier cholesterol balance, and smoother circulation. Studies also link 250 to 500 mg of EPA and DHA per day with a lower risk of heart disease.
Here is what happens to your body when you take omega-3 everyday for your heart, and how consistency turns small daily actions into lasting protection.
Lowers Inflammation to Protect Your Arteries
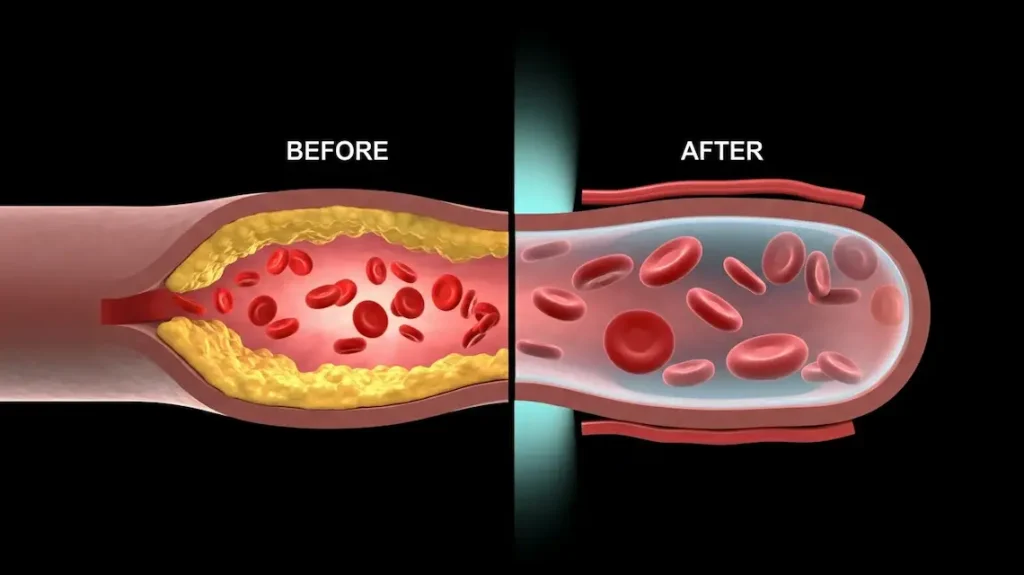
Chronic inflammation is like rust inside your arteries. It irritates vessel walls, invites plaque buildup, and makes blood flow turbulent. EPA and DHA help by producing anti-inflammatory compounds that calm this process. They reduce signaling molecules that trigger swelling in vessel linings, so your arteries stay more flexible and clear.
Daily omega-3 intake is tied to lower C-reactive protein, a common blood marker of inflammation. In several trials, people taking fish oil or algae-based omega-3s saw CRP levels trend down after consistent use. Lower CRP means less inflammatory pressure on your arteries, which supports better blood pressure control and a healthier pulse.
There is also a blood-thinning effect that benefits circulation. Omega-3s make platelets less sticky, so clots are less likely to form. Blood flows more smoothly, which reduces stress on your heart with every beat.
You will not feel all of this in a week. But by week 4 to 8, the body adapts. Vessel walls relax, plaques are less prone to rupture, and the overall environment shifts from inflamed to stable. That is a safer setting for your heart every single day.
A few practical steps to make it work:
- Take omega-3 with a meal that contains fat for better absorption.
- Aim for a combined 250 to 500 mg of EPA and DHA daily if you are healthy. Higher doses may be used for triglyceride support under medical guidance.
- Pair omega-3s with a produce-forward plate and steady movement for even stronger blood pressure and artery benefits.
Balances Cholesterol and Triglycerides Over Time
Omega-3s do two big jobs for your lipid profile. They lower triglycerides and support better cholesterol balance. Triglycerides drop because omega-3s reduce the liver’s production of VLDL particles that carry these fats. Less VLDL means fewer triglycerides in your bloodstream and fewer leftovers that can turn into small, dense LDL.
On the cholesterol side, daily omega-3s often raise HDL, the helpful particle that ferries cholesterol away from arteries. LDL can shift in a better direction too. Over time, LDL particles may become larger and less likely to lodge in vessel walls. That combination lowers the load of fatty deposits and keeps blood moving more freely.
The timeline matters. In the first 2 to 4 weeks, triglycerides tend to move first. By 8 to 12 weeks, HDL improvements show up more clearly on labs. Keep going and the benefits compound. Better lipids reduce plaque growth, which lowers the chance of artery blockages and the events that follow.
To support results that last:
- Choose a consistent daily dose. Most people do well with 250 to 500 mg of EPA and DHA per day from fish oil or algae oil.
- Make room for fatty fish twice per week. Try salmon, sardines, trout, or mackerel. For meal ideas, check out foods to boost HDL cholesterol.
- Read your label. Look for the actual EPA and DHA amounts, not just “fish oil” milligrams.
- Stay steady. Lipid changes build with routine use and a heart-smart plate.
Bottom line, daily omega-3s create a healthier setting inside your blood vessels. Inflammation cools, plaque is less likely to grow or rupture, and your lipid panel trends in the right direction. That is how better circulation shows up day after day, and why a steady dose links to lower heart disease risk over time.
Boosts Brain Function and Mood with Regular Omega-3 Intake
Your brain runs on fat. The membranes that wrap your neurons are rich in DHA, and they set the stage for fast, clear signaling. When you take omega-3s daily, these fats slot into cell membranes, increase fluidity, and support the receptors that handle your thoughts and feelings. That is a simple way to picture what happens to your body when you take omega-3 everyday.
EPA pulls its weight too. It helps calm cytokines that stir up inflammation, which can blur thinking and weigh down your mood. Together, EPA and DHA help you think sharper, remember more, and feel more even across the day. For a broader view on how food fats affect mood chemistry, you can explore healthy fats for mood regulation.
What might you notice with steady intake? Clearer focus during work, easier recall of names, and less mental fatigue late in the afternoon. These wins build over weeks as your brain updates its membranes and signaling pathways.
Enhances Memory and Learning Abilities
Omega-3s support the hippocampus, the brain’s memory hub. The hippocampus is packed with DHA-rich membranes that guide synapse formation and plasticity. When DHA is available every day, neurons communicate more smoothly, and the signals that encode new memories get through with less static.
In human trials, older adults who took daily omega-3s often showed:
- Better verbal recall, like lists or names
- Faster learning on new tasks and improved attention
- Modest gains on executive function tests over several months
Why it works comes down to structure and signaling:
- Membrane fluidity: DHA keeps neuron membranes flexible, which improves receptor shape and function.
- Synaptic plasticity: Omega-3s help maintain proteins that form and remodel synapses, key for learning.
- Neuroinflammation control: EPA supports anti-inflammatory pathways that protect hippocampal cells.
What can you expect with steady use?
- Weeks 2 to 4: Subtle improvements in mental clarity and focus, especially in the morning.
- Weeks 6 to 12: Noticeable gains in recall and learning. You may find it easier to retain what you study or remember details from meetings.
- Month 3 and beyond: Benefits hold as membranes turn over and stabilize with higher DHA content.
Practical tips to lock in results:
- Take your omega-3 with a meal that includes fat for better absorption.
- Aim for a daily combined intake of DHA and EPA that fits your goals and diet. Many people start with 250 to 500 mg combined, while some choose higher ranges after talking with a professional.
- Pair with brain-positive habits like brisk walks, quality sleep, and targeted practice. Consistency multiplies the effect.
Eases Depression and Improves Emotional Balance
Mood is chemistry and communication. Omega-3s support both. Daily intake helps regulate serotonin signaling by improving receptor function in neuron membranes and may influence how serotonin is released and reabsorbed. EPA’s anti-inflammatory effect can also lower neuroinflammatory stress that drags mood down.
Research across clinical trials shows that 1 to 2 grams per day of omega-3s, often with higher EPA relative to DHA, can reduce depressive symptoms over several months. Many participants report fewer low days, less anxiety, and better stress tolerance. Results tend to grow with time, not overnight.
Here is how omega-3s help your emotional balance:
- Neurotransmitter support: Healthier membranes improve how serotonin and dopamine receptors respond.
- Inflammation control: EPA lowers inflammatory signals linked with low mood and brain fog.
- Stress-circuit resilience: DHA supports brain regions involved in emotional regulation and executive control.
What you may feel with daily use:
- Calmer mornings and fewer mood dips in the late afternoon
- Lower reactivity in tense moments, with faster recovery after stress
- A steadier outlook that makes habits like exercise and sleep easier to keep
To set yourself up for success:
- Consider a daily dose in the 1 to 2 gram range for mood support, often with an EPA focus. Work with a clinician if you take medications or have a condition.
- Take your omega-3 at the same time each day with food. Consistency matters for membrane turnover.
- Support the basics that shape mood, like your sleep schedule and meals. If low mood lingers, these nutrition strategies against low mood can help you build a stronger base.
Everyday example: You start the week with a packed schedule. After two to three months of steady omega-3s, your head feels clearer at 3 p.m., you finish tasks without circling back, and you handle tense emails without a spiral. That is your brain using better building blocks to do its job.
Key takeaways to remember:
- DHA builds brain cell membranes that drive memory and focus.
- EPA helps calm inflammation tied to depression and anxiety.
- Daily intake supports serotonin function, which steadies mood over time.
- Benefits grow with consistent use, usually over 6 to 12 weeks.
Reduces Joint Pain and Inflammation Throughout Your Body
Daily omega-3 helps turn down the body’s inflammatory alarms. EPA and DHA shift your cells toward making anti-inflammatory mediators, like resolvins and protectins, while dialing back COX and LOX pathways that create pain-driving prostaglandins and leukotrienes. The result is less swelling, less stiffness, and smoother movement from head to toe. If you have wondered what happens to your body when you take omega-3 everyday, this is one of the most noticeable benefits.
Relieves Arthritis Symptoms for Easier Movement
Arthritic joints often feel dry and tight. Omega-3 supports healthier joint lubrication by improving the quality of synovial fluid, the slick liquid that cushions cartilage. When inflammation drops, the joint capsule holds less fluid, so swelling comes down and you move with less friction.
Several trials in people with rheumatoid arthritis report less morning stiffness and joint tenderness with daily omega-3. Many used around 2 to 3 grams per day of EPA and DHA combined. Participants often reduced pain scores and used fewer pain meds over time. The relief builds as inflammatory chemicals decline and pro-resolving compounds rise.
Make your daily routine work harder:
- Dose smart: Many adults do well with 1 to 3 grams of combined EPA and DHA for joint relief. Start on the lower end and adjust with guidance if needed.
- Time with meals: Take omega-3 with food that contains fat to improve absorption.
- Pick your source: Fatty fish like salmon, sardines, trout, and mackerel. Plant foods like walnuts and ground flax provide ALA, which the body converts at a low rate. For reliable EPA and DHA, use fish oil or algae oil.
- Combine with a joint-friendly plate: Focus on a colorful, produce-forward diet. Add olive oil, herbs, and spices that fight inflammation, such as turmeric and ginger.
- Support cartilage: Keep moving. Gentle strength work and walking feed cartilage through pressure and release, especially when inflammation is lower.
Signs you are on the right track:
- Less morning stiffness within 2 to 4 weeks
- Easier grip and knee bend by weeks 6 to 8
- Fewer flares with steady intake and a consistent diet
Small changes help. Swap one red meat meal for salmon twice a week. Add a handful of walnuts to afternoon yogurt. If you use a supplement, choose a product that lists exact EPA and DHA per serving, not just fish oil milligrams.
Speeds Up Muscle Recovery After Workouts
Hard training sparks micro-tears in muscle fibers. Inflammation clears the damage, but too much drives soreness and slows your next session. Omega-3 helps control this response. EPA and DHA shift cell signaling toward resolution, which cuts excess swelling and reduces delayed onset muscle soreness.
Studies in trained athletes and active adults show daily omega-3, often 2 to 3 grams of combined EPA and DHA, can:
- Reduce soreness 24 to 72 hours after intense sessions
- Preserve strength and range of motion after eccentric work
- Lower blood markers of muscle damage and inflammation
Why it works:
- Cell membrane support: Omega-3s integrate into muscle cell membranes, which may stabilize cells during heavy loads.
- Balanced inflammation: EPA reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines that prolong soreness.
- Faster resolution: Pro-resolving mediators help clear debris so new tissue can rebuild.
Simple steps to recover faster:
- Take your omega-3 daily, not just on training days. Consistency sets the baseline.
- Pair with protein after workouts. Aim for 20 to 30 grams within one hour.
- Eat antioxidant-rich foods. Berries, citrus, leafy greens, and peppers support recovery.
- Hydrate and sleep. These basics multiply the anti-inflammatory effect.
- Use active recovery. Easy cycling or walking speeds circulation without adding stress.
What you might notice:
- Less next-day stiffness after legs or pull days
- Quicker return to peak effort later in the week
- Fewer lingering aches in smaller joints, like wrists and ankles
Natural sources still count. Try salmon tacos after a lift, sardines on whole-grain toast, or a trout salad with olive oil. If you do not eat fish, algae oil delivers EPA and DHA without the fish taste. Stay consistent for at least 6 to 8 weeks to feel the full benefit.
Key takeaways:
- Omega-3 calms joint and muscle inflammation, which lowers pain and swelling.
- 2 to 3 grams of EPA and DHA daily often helps arthritis symptoms and post-workout soreness.
- Food first, supplements as needed. Combine both with a smart diet, steady training, and good sleep for real-world results.
Improves Skin Glow and Eye Health from Daily Omega-3
Glowing skin and clear, comfortable eyes often come down to healthy cell membranes. Omega-3s build those membranes and calm the low-grade inflammation that dries tissue out and dulls your look. If you have wondered what happens to your body when you take omega-3 everyday, you will notice steady changes in how your skin holds moisture and how your eyes feel from morning to night.
Hydrates Skin and Fights Signs of Aging
Omega-3s strengthen your skin barrier, the outer layer that keeps water in and irritants out. When EPA and DHA join your skin cell membranes, they improve fluidity and help prevent transepidermal water loss. The result is a plumper, smoother look that holds through the day.
Daily intake also supports collagen. By dialing down collagen-degrading enzymes and inflammatory signals, omega-3s help preserve the scaffolding that keeps skin firm. Research links regular omega-3 intake with better skin elasticity and fewer rough patches, especially in dry environments.
Here is what this looks like over time:
- Weeks 2 to 3: Less tightness after cleansing, fewer dry flakes.
- Weeks 4 to 6: Smoother texture, a soft glow, fine lines look less sharp.
- Month 2 and beyond: More even tone and better bounce when you press the cheek.
Omega-3s can also help with breakouts. They reduce inflammatory cytokines that drive red, tender blemishes and may improve insulin sensitivity, which steadies oil production. That combo often means calmer, clearer skin.
Simple ways to support a youthful look:
- Eat fatty fish twice a week or use an algae or fish oil supplement.
- Pair omega-3s with a gentle moisturizer and a daily SPF.
- Fill your plate with produce and minerals that support collagen, like vitamin C and zinc.
- Explore food ideas that pair skin-friendly produce with healthy fats in this guide on food for clearer glowing skin.
Helpful skin cues to track:
- Morning tightness eases after cleansing.
- Makeup sits better and creases less by mid-afternoon.
- Redness and post-acne marks fade more evenly.
When winter hits or indoor heat runs, bolster your routine with diet tweaks that feed your moisture barrier. For seasonal support, see these remedies for dry skin hydration.
Key takeaways:
- Barrier strength improves, so skin holds water longer.
- Collagen stays more intact, which softens lines and sag.
- Calmer pores often mean fewer angry breakouts.
Protects Eyes from Dryness and Age-Related Issues
Your eyes rely on a stable tear film. Omega-3s support the oily layer made by the meibomian glands, which keeps tears from evaporating too fast. With better oil quality, tears spread evenly across the surface, so blinking feels smooth and screens bother you less.
Daily omega-3s also help protect delicate eye tissues. EPA and DHA act as building blocks for retinal cell membranes and support antioxidant pathways that counter light and oxidative stress. Research links higher omega-3 intake, especially DHA, with a lower risk of age-related macular degeneration over time.
What you may notice with steady intake:
- Less scratchy or gritty feeling by afternoon.
- Fewer reflex tears in wind or air conditioning.
- Clearer, more stable vision during long work sessions.
Practical habits that support eye comfort:
- Take omega-3 with a meal that contains fat to improve absorption.
- Use the 20-20-20 rule on screens to reduce strain.
- Add leafy greens, citrus, and colorful produce for extra antioxidants.
- Stay hydrated to support tear volume.
Why this works:
- Tear film stability improves when the oily layer is healthier.
- Retinal support from DHA helps keep cell membranes flexible.
- Oxidative stress control reduces wear on the macula as you age.
The payoff builds with time. Many people feel less dryness in 3 to 4 weeks. By 2 to 3 months, comfort and clarity feel more consistent, even in dry offices or on long drives.
A steady omega-3 habit is a simple way to look and feel more vibrant. Skin glows, eyes stay comfortable, and you carry an easy, rested look into each day. That is real-world vitality you can see in the mirror and feel behind your eyes.
Conclusion
Daily omega-3s add up to real change. A steadier heart, a sharper mind, calmer joints, and healthier skin and eyes are the core wins. That is what happens to your body when you take omega-3 everyday, and it grows with consistency.
Keep it simple. Aim for 250 to 1000 mg of combined EPA and DHA per day. Choose salmon, sardines, trout, or mackerel a few times a week, or use a quality fish oil or algae oil. Plant foods help too. If you take medications or have a condition, check in with your doctor first.
Start today and track how you feel over 30 days. Notice energy, focus, joint comfort, and skin hydration. Small daily steps can reset how you move, think, and recover.
If this helped, share your experience or your best tips. Your story may be the nudge someone needs to begin.
FAQ: Daily Omega-3
How does taking omega-3 daily affect heart health?
It supports heart health. EPA and DHA can lower triglycerides, slightly reduce blood pressure, and help keep arteries less inflamed. Benefits build with steady intake.
Will it lower my triglycerides?
Yes, often by 20 to 50 percent at higher doses. Prescription-strength omega-3 works best for high triglycerides. Work with your clinician on dose and follow-up labs.
Does omega-3 change LDL or HDL?
It can raise LDL a little in some people, mainly with fish oil. HDL may rise a bit. Net effect still favors heart health when triglycerides drop.
Can it help with inflammation and joint pain?
It can ease inflammatory pain for some, especially in rheumatoid arthritis. Relief may take 6 to 12 weeks. It is not a painkiller, it supports lower inflammation.
What about mood and brain function?
Evidence is mixed. Some people notice better mood or less anxiety, especially with EPA-focused formulas. Cognitive benefits in healthy adults are small, but may help those with low intake.
Does it help with eye dryness?
Many people with dry eye feel less irritation with daily omega-3. Results vary by dose and the severity of symptoms. Give it at least 8 to 12 weeks.
Will my skin change?
Skin may feel less dry or flaky, and redness can ease. Effects are modest and take time. Pair with good skincare and hydration.
Can omega-3 affect weight or metabolism?
It does not cause weight loss. It may slightly improve insulin sensitivity in some cases. The larger effect is on triglycerides and liver fat, not the scale.
Is there a bleeding risk?
At typical doses, risk is low. High doses can increase bleeding time. If you take blood thinners, high-dose aspirin, or have surgery planned, talk to your clinician first.
What about heart rhythm risks?
Very high doses, often 4 grams per day or more, have been linked to a small rise in atrial fibrillation in some studies. If you have a history of AFib, discuss dosing with your cardiologist.
How soon will I notice changes?
Blood triglycerides can shift in 4 to 8 weeks. Joint and eye benefits may take 8 to 12 weeks. Heart protection builds over months to years.
How much should I take daily?
For general health, 250 to 500 mg EPA plus DHA per day is common. For high triglycerides, 2 to 4 grams per day is used under medical care. Follow labels or a clinician’s advice.
What’s the difference between fish oil, algae oil, and flax?
Fish and algae oils give EPA and DHA directly. Flax and chia give ALA, which the body converts poorly. Algae oil suits vegetarians, and it avoids marine contaminants.
Are there side effects?
Some people get fishy burps, nausea, or soft stools. Taking capsules with a meal, splitting doses, or using enteric-coated forms can help. Refrigerate liquids to keep them fresh.
Do supplements contain mercury?
Refined fish oil is purified, so mercury is not a concern. Whole fish can contain mercury, especially large predatory fish. Algae oil avoids this issue entirely.
Does the form matter for absorption?
Absorption improves with a fatty meal. Triglyceride and re-esterified triglyceride forms absorb well. Ethyl ester forms also work, just pair with food for better uptake.
Can I take it with other supplements or meds?
It usually pairs well with vitamin D and magnesium. Be careful if you take anticoagulants, high-dose aspirin, or anti-platelet drugs. Check for interactions with your clinician.
Is daily omega-3 safe in pregnancy and breastfeeding?
Yes, and it supports fetal brain and eye development. Choose algae oil or purified fish oil, and avoid supplements with added vitamin A unless advised.
What if I eat fatty fish often?
If you eat salmon, sardines, trout, or mackerel 2 to 3 times per week, you may not need a supplement. Track total intake of EPA and DHA for clarity.
Can kids take omega-3?
Yes, with kid-appropriate doses and products. It can help children who eat little fish. Ask a pediatrician for dosing by age and weight.
How do I pick a quality product?
Look for third-party testing, clear EPA and DHA amounts, and a recent expiration date. Choose brands that share contaminant and oxidation results. Store in a cool, dark place.
What happens if I stop taking it?
Blood levels fall within weeks. Triglycerides may rise back, and symptom relief can fade. Consistency matters.
Who should avoid or use caution?
People with shellfish allergies, bleeding disorders, or planned surgery need guidance. Those with AFib or on blood thinners should review dosing with a clinician. Diabetics can use it, but monitor lipids and glucose.
Can I overdose on omega-3?
Extremely high intakes can raise bleeding risk, suppress immunity, or cause GI upset. Stay within labeled doses unless your clinician prescribes a higher amount.

Gas S. is a health writer who covers metabolic health, longevity science, and functional physiology. He breaks down research into clear, usable takeaways for long-term health and recovery. His work focuses on how the body works, progress tracking, and changes you can stick with. Every article is reviewed independently for accuracy and readability.
- Medical Disclaimer: This content is for education only. It doesn’t diagnose, treat, or replace medical care from a licensed professional. Read our full Medical Disclaimer here.