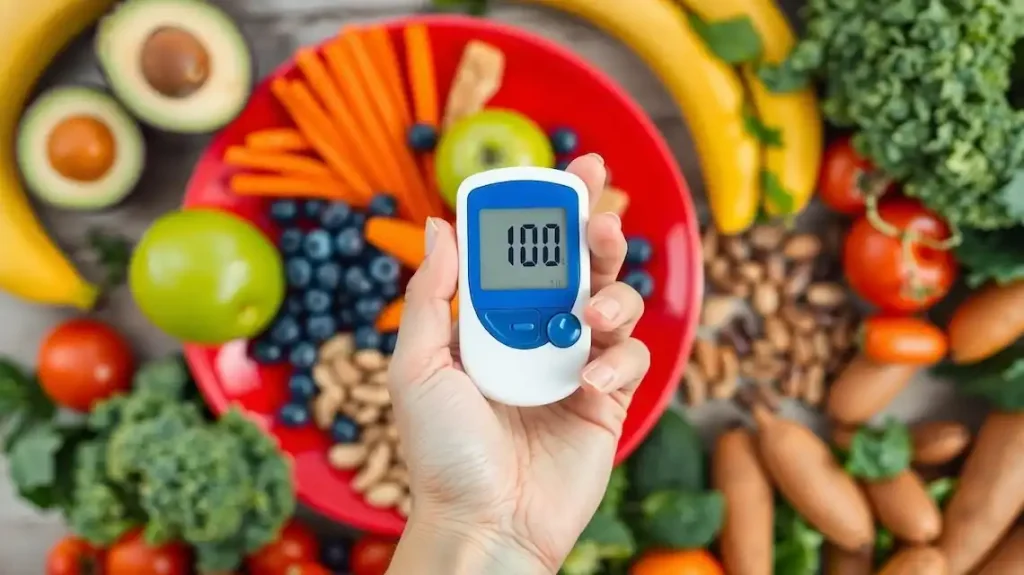
Keeping your blood sugar stable isn’t just for those with diabetes, it’s an everyday game plan for anyone who wants steady energy and better health. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the main fuel your body pulls from food to keep you moving and thinking. But when these levels spike or drop, you might feel sluggish, irritable, or even dizzy.
Stable blood sugar plays a big part in managing cravings and staying focused throughout your day. People with diabetes, prediabetes, or anyone aiming for balanced energy will benefit from simple changes to what they eat. Choosing the right foods to keep blood sugar stable helps you avoid those mid-afternoon crashes and supports long-term health.
Food choices matter a lot here. Smart habits and picking foods that digest slowly are key steps for feeling your best. If you’re curious about how what you eat affects your mood, check out the effects of healthy eating on mood. Let’s break down how the right foods can give you stable energy and set you up for a better day.
Understanding Blood Sugar Stability
Blood sugar stability means your glucose levels stay within a healthy range instead of jumping up or crashing down. Your body depends on a steady supply of glucose for energy. Insulin, a hormone made by your pancreas, helps your cells absorb this glucose from your blood. When blood sugar swings too high, your body works overtime to fix it, which often leads to an energy rollercoaster and mood crashes. When it gets too low, you might feel weak, shaky, or even anxious. Let’s explore how daily habits and foods to keep blood sugar stable play a role in your health.
How Blood Sugar Levels Fluctuate
What you eat, when you eat, and how much you eat all shape your blood sugar curve. Different foods get digested at different speeds. Foods high in refined sugar and simple carbs cause a quick spike in blood glucose, followed by a rapid drop that can leave you drained. On the other hand, meals rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats help slow down digestion so your body absorbs glucose gradually.
Here are some key factors that influence your blood sugar:
- Carbohydrate type: White bread, pastries, and sugary drinks lead to fast spikes. Whole grains, beans, and vegetables digest slower.
- Meal timing: Skipping meals or eating at odd hours can trigger sharp blood sugar dips or sudden spikes when you do eat.
- Portion sizes: Oversized portions, even of healthy foods, can bump glucose levels higher than your body needs.
- Food combinations: Pairing carbs with protein or fat softens blood sugar jumps. A snack of fruit and nuts will affect your body differently than fruit alone.
Learning how these factors impact your body can help you build meals and snacks that encourage balance and prevent those highs and lows.
Why Stable Blood Sugar Matters for Everyone
Stable blood sugar isn’t just important for people with diabetes. When glucose stays steady, everyone benefits—from your mind to your physical health. Fluctuating blood sugar levels pull your energy up and drag it back down, often leaving you tired or cranky. Unstable levels can even impact your mood, raising stress and frustration or causing brain fog.
Here’s why stable blood sugar truly matters:
- More consistent energy: You avoid “crashes” that make you want to nap after lunch or raid the snack drawer mid-afternoon.
- Better mood control: When glucose flows steadily, you feel calmer and more balanced. Foods to keep blood sugar stable support better focus and a better outlook. For example, the impact of healthy fats on emotional well-being is well-documented.
- Lower risk for health problems: Over time, frequent spikes and drops increase the risk for insulin resistance, prediabetes, heart problems, and weight gain.
- Support for brain health: Your brain relies on a stable stream of glucose. Unstable sugar can leave you foggy, distracted, or on edge.
Eating meals that focus on balance, like those described in the Plant-Based Diet, naturally supports blood sugar control and overall emotional health.
Prioritizing foods to keep blood sugar stable pays off every day, helping you feel your best both physically and emotionally. Steadier glucose means steadier energy, a better mood, and less risk of long-term health setbacks.
Best Foods to Keep Blood Sugar Stable
Choosing the right foods is the foundation for steady blood sugar. By focusing on meals rich in fiber, lean protein, and healthy fats, your body gets a slow, steady release of energy. Let’s break down the food groups that work best. Each type has a unique benefit and can easily fit into daily meals, making it realistic to eat in a way that keeps you feeling balanced all day. Here are some of the most effective foods to keep blood sugar stable and tips for making them a regular part of your routine.
High-Fiber Foods: Vegetables, Legumes, and Whole Grains
Fiber plays a powerful role in blood sugar control. It acts like a traffic light for glucose, slowing down how fast sugar enters your bloodstream. This helps avoid big spikes and keeps your energy steady. Meals high in fiber also take longer to digest, which means you stay full longer.
Some of the best high-fiber foods to keep blood sugar stable include:
- Oats: Steel-cut or old-fashioned oats are rich in soluble fiber. This type of fiber forms a gel in your gut that slows sugar absorption.
- Beans and lentils: Black beans, chickpeas, and lentils are packed with fiber and protein. They’re perfect for soups, stews, and salads.
- Whole fruits: Apples, pears, oranges, and berries all offer natural sweetness plus plenty of fiber, thanks to their edible skins and pulp.
- Whole grains: Brown rice, quinoa, barley, and whole wheat bread fill you up without causing a glucose spike.
Easy ways to boost your fiber intake:
- Add beans or lentils to salads and soups.
- Start your day with oatmeal instead of sweetened cereal.
- Snack on whole fruit, not juice.
- Swap white rice for brown, or try quinoa and barley.
For more gut-friendly options that encourage overall health and help with digestion, check out these foods that support gut health.
Lean Proteins: Meat, Fish, Eggs, and Plant-Based Options
Protein is another ally for stable blood sugar. It has almost no direct impact on blood sugar itself, but it slows the digestion of carbs and blunts spikes in glucose after meals. Protein also makes meals more satisfying, which can help prevent overeating or snacking on sweets later.
Reliable lean protein sources:
- Chicken breast and turkey
- Fish like salmon, cod, or sardines
- Eggs
- Greek yogurt
- Plant-based options: Tofu, tempeh, legumes, and protein-rich grains like quinoa
Pairing protein with fiber and healthy fat delivers a one-two punch for blood sugar balance. For example, a lunch of grilled chicken with roasted veggies and quinoa leaves you energized for hours.
Plant-based eaters have plenty of choices, too. If you want more ideas, dive into these plant-based protein sources for meals that are gentle on blood sugar.
Healthy Fats: Nuts, Seeds, and Avocados
Not all fats are the same. Healthy fats play a key role in blood sugar stability by slowing down the absorption of sugars, so glucose drifts into your bloodstream rather than rushing in all at once. They also satisfy hunger and support heart health.
Easy sources of healthy fats include:
- Nuts: Almonds, walnuts, pistachios, and pecans
- Seeds: Chia, flax, pumpkin, and sunflower seeds
- Avocado: Creamy and easy to add to toast, salads, or smoothies
- Olive oil: Great for drizzling over vegetables or as a salad dressing base
Simple ways to add healthy fats to meals:
- Sprinkle seeds over morning oats or yogurt.
- Slice avocado into salads or whole-grain toast.
- Snack on a handful of nuts between meals.
- Use olive oil for homemade dressings.
Foods to Limit or Avoid for Blood Sugar Stability
Some foods make blood sugar management much harder. Processed sugars, refined grains, and sweetened drinks give you a rush of energy followed by a crash. These quick-digesting foods skip the body’s normal slow-release system, flooding your bloodstream with glucose.
Major culprits include:
- Sugary snacks: Candy, baked goods, and sweet breakfast cereals
- Refined grains: White bread, white rice, regular pasta, and most crackers
- Sugar-sweetened drinks: Soda, fruit punch, and most flavored coffees
Tips to avoid blood sugar spikes from these foods:
- Swap white bread and rice for whole grain versions.
- Choose water, herbal tea, or unsweetened beverages over soda and sweetened coffees.
- Read ingredients—watch for names like “high fructose corn syrup,” “maltose,” or “evaporated cane juice.”
Ready to take it further? Get practical help with cutting out processed sugar so you’ll have more steady days and fewer crashes. Making these changes gives you a huge edge in controlling cravings, improving focus, and feeling your best every day.
Lifestyle Strategies to Enhance Blood Sugar Control
While foods to keep blood sugar stable set the tone, your daily routines and habits play an equal part in the blood sugar story. Think of your body as a car: the fuel (food) matters, but so do the way you drive and maintain it. Embracing small changes in movement, stress management, and mindful eating can make blood sugar control feel natural instead of like a constant battle.
Physical Activity and Blood Sugar Management
Physical movement acts like a natural helper for blood sugar stability. When you work your muscles—walking, cycling, taking the stairs—your cells open up to glucose more efficiently. This not only lowers glucose in your blood right away, but it also improves insulin sensitivity over time, making your body better at handling carbs you eat.
You don’t have to run marathons to see results. Even moderate activities, like going for a stroll after a meal, have benefits. For example, just a 10-15 minute walk after eating can help your body process glucose more smoothly. Curious about why this works? Dive into the benefits of walking after eating, including how walking boosts digestion and prevents big blood sugar jumps.
To keep it easy and enjoyable:
- Aim for 20–30 minutes of movement most days.
- Break it up—three 10-minute walks work just as well as one 30-minute session.
- Choose activities you enjoy, like dancing, gardening, or biking.
- Use a fitness tracker, pedometer, or even your phone to watch your progress.
Adding regular movement can also keep energy steady, lift your mood, and make it easier to stick with healthy food choices—all important for keeping blood sugar stable every day.
Managing Stress and Getting Adequate Sleep
Mental health and physical health are tightly linked when it comes to blood sugar. Stress releases hormones (like cortisol) that signal your body to release extra glucose into the blood. If stress is constant, this can keep blood sugar stuck at higher levels.
Poor sleep has a direct impact too. Even one night of tossing and turning can raise your body’s stress response, which often leads to cravings for sugary foods and less motivation to move or eat well. Over time, short or restless sleep can raise your risk for insulin resistance.
Here’s how you can start breaking the cycle:
- Practice nightly routines that make it easier to fall asleep (keep your room cool, skip screens before bed, set a regular bedtime).
- Try relaxation techniques for stress, like deep breathing, gentle yoga, or short guided meditations.
- Take short breaks throughout your day to stretch, breathe, or just pause.
Small stress-busting steps and better sleep make it easier to stick with habits and foods to keep blood sugar stable. Both give your body a chance to reset and repair.
Monitoring and Mindful Eating
Paying attention to how, when, and what you eat can work wonders for balance. Eating mindfully means being present at meals and listening to your own body’s signs and rhythms rather than rushing or eating because of stress.
Start with the basics:
- Keep a food diary: Write down what you eat and how it makes you feel. Patterns will pop up—certain foods (or skipping meals) might lead to cravings or energy crashes.
- Practice portion control: Use smaller plates, pause before seconds, and check in midway through a meal to see if you’re full.
- Tune in to hunger cues: Ask yourself if you’re truly hungry or just bored, stressed, or tired before reaching for snacks.
- Eat slowly: Take your time chewing. It helps your body register fullness and makes meals more enjoyable.
Mindful eating helps you spot your personal triggers and recognize which habits support stable energy and which knock you off course. When paired with smart food choices and movement, it’s one of the simplest ways to keep blood sugar on track.
Healthy routines, think movement, restful sleep, stress care, and mindfulness—rarely succeed without support from what you eat. And with the right lifestyle mix, foods to keep blood sugar stable can do their job even better.
Conclusion
Choosing foods to keep blood sugar stable is a smart move for anyone wanting more energy and better overall health. Filling your meals with fiber, protein, and healthy fats helps your body avoid dramatic glucose swings, letting you feel steady all day. Blending these foods with movement, good sleep, and mindful eating makes these results last.
Lasting change starts with small, daily steps. Whether you try one new snack or adjust your weekly meal plan, each choice makes a difference. For even more ways to support steady energy, consider the health benefits of fermented foods and how they fit into a balanced routine.
Your habits shape your health, and each positive change stacks up over time.
FAQ:
What foods help keep blood sugar steady throughout the day?
High-fiber foods like beans, lentils, oats, non-starchy vegetables, and whole grains slow down sugar absorption. Lean protein from poultry, fish, eggs or tofu can also help, as can healthy fats from nuts, seeds, and avocado.
Are there specific snacks that prevent blood sugar spikes?
Pair protein or healthy fat with carbs for snacks. Try apple slices with almond butter, plain Greek yogurt with berries, or whole grain crackers with cheese. This keeps sugar levels steady between meals.
Should I avoid fruit because of the sugar?
You don’t need to skip fruit, but choose whole fruits instead of juice. Whole fruits have fiber, which slows sugar uptake. Berries, apples, pears, oranges, and peaches are all good options.
Can certain drinks help manage blood sugar?
Water is best. Unsweetened tea and black coffee are fine in moderation. Avoid sugary drinks, fruit juice, and regular sodas—they can spike blood sugar quickly.
Which grains are best for blood sugar control?
Whole grains beat refined grains. Eat brown rice, quinoa, barley, steel-cut oats, and whole wheat bread. Skip white bread, white rice, and other highly processed grains.
How much does portion size matter for blood sugar?
Portion size matters a lot. Eating too much—even of healthy food—can push blood sugar up. Use smaller plates and pay attention to hunger signals.
Does eating on a schedule help stabilize blood sugar?
Yes. Eating regular meals and snacks about every 3 to 4 hours keeps blood sugar balanced and prevents big drops or spikes.
What foods should I limit to avoid blood sugar swings?
Cut back on sweets, baked goods, white bread, sugary cereals, regular pasta, and fried foods. These raise blood sugar quickly and can lead to crashes later.
Are healthy fats important for blood sugar balance?
Yes. Unsaturated fats from nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fish help slow digestion and keep blood sugar even. Avoid trans fats and limit saturated fats.
Do artificial sweeteners affect blood sugar?
Most artificial sweeteners don’t raise blood sugar directly, but some people find they increase cravings for sweets. Use them sparingly and focus on whole foods.
Should I eat differently if I have type 2 diabetes or prediabetes?
A balanced diet with fiber, lean protein, healthy fat, and limited refined carbs is key for most people. If you have diabetes or prediabetes, work with your doctor or dietitian for personalized advice.

Gas S. is a health writer who covers metabolic health, longevity science, and functional physiology. He breaks down research into clear, usable takeaways for long-term health and recovery. His work focuses on how the body works, progress tracking, and changes you can stick with. Every article is reviewed independently for accuracy and readability.
- Medical Disclaimer: This content is for education only. It doesn’t diagnose, treat, or replace medical care from a licensed professional. Read our full Medical Disclaimer here.